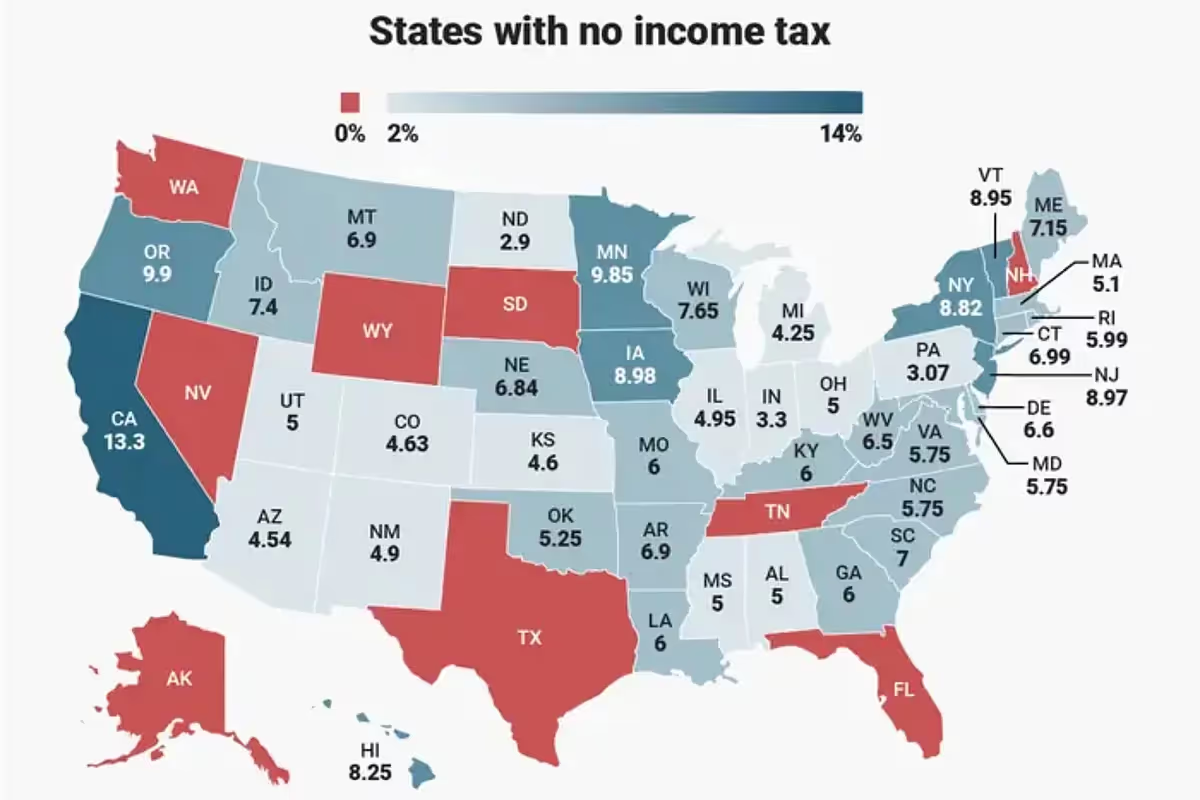
Sales tax is a significant consideration for businesses and consumers alike, influencing purchasing decisions and even where companies choose to operate. While most U.S. states impose sales tax at varying rates, five states stand out by not charging a state-level sales tax at all. These states are Alaska, Delaware, Montana, New Hampshire, and Oregon. However, each has its own nuances that are important to understand.
Which U.S. States Have No Sales Tax?
The following states do not impose a statewide sales tax, making them appealing for shoppers and business owners looking to minimize their tax burden:
Alaska (Has Local Sales Tax but No State-Level Sales Tax)
Alaska does not have a statewide sales tax, but it does allow local jurisdictions to impose their own sales taxes. This means that while some areas in Alaska have a 0% sales tax, others may have local taxes that businesses and consumers must account for.
- Local Tax Considerations: Many municipalities in Alaska levy their own sales taxes, which can range from 1% to 7.5%.
- Business Perspective: Companies operating in Alaska must be aware of the local tax rates where they do business. Even if a business is located in a tax-free area, online sales to localities that charge tax may still be subject to taxation.
- Consumer Impact: Consumers benefit from no statewide sales tax but should check local tax rates before making major purchases.
Delaware
Delaware is often referred to as a tax haven because it does not impose a state-level sales tax. This makes it a popular state for businesses looking to minimize tax obligations, especially for corporations.
- Why Businesses Choose Delaware: Many companies incorporate in Delaware due to its business-friendly regulations, tax advantages, and efficient legal system.
- Consumer Benefits: Shoppers in Delaware do not have to pay sales tax, making it a great destination for major purchases, including electronics, cars, and other big-ticket items.
- Other Taxes: While Delaware does not charge sales tax, it does impose a gross receipts tax on businesses, which is based on revenue rather than profits.
Montana
Montana has no state or local sales tax, making it one of the most tax-friendly states for both residents and businesses.
- Tourist Consideration: Montana’s lack of sales tax attracts tourists who take advantage of tax-free shopping, particularly for expensive items.
- Business Perspective: Businesses operating in Montana can sell goods without collecting sales tax, making it a prime location for online retailers looking to reduce tax complexity.
- Alternative Taxation: Montana funds its government through income tax and property taxes instead of sales tax.
New Hampshire
New Hampshire does not impose a state sales tax, making it an attractive place for shoppers and businesses. However, there are other taxes to consider.
- Retail & Business Advantage: Many businesses leverage New Hampshire’s tax-free status to attract customers from neighboring states like Massachusetts, which has a 6.25% sales tax.
- Use Tax Concerns: Residents of nearby states who shop in New Hampshire may be required to pay a use tax in their home state if they bring taxable goods across state lines.
- Other Taxes: New Hampshire has higher property taxes and a business profits tax, which help offset the lack of sales tax revenue.
Oregon
Oregon is another state that does not impose sales tax, making it a great location for businesses and consumers looking to save money.
- Retail & E-Commerce Benefits: Many online retailers operate from Oregon to avoid collecting sales tax in their home state.
- Tax Structure: Oregon relies on income tax and business taxes instead of sales tax to fund government operations.
- Consumer Perspective: Shoppers in Oregon enjoy tax-free purchases on all goods, making it a popular place for cross-border shopping.
Why Businesses in States with No Sales Tax May Still Need to Collect Sales Tax
Even if a business is based in a state with no sales tax, it may still be required to collect sales tax when selling to customers in other states. This is due to economic nexus laws, which require businesses to collect and remit sales tax if they meet certain sales thresholds in another state.
- Economic Nexus Laws: Many states have adopted economic nexus laws that require businesses to collect sales tax if they surpass a specific revenue or transaction threshold.
- Marketplace Sellers: If you sell on platforms like Amazon, Etsy, or eBay, these marketplaces may collect sales tax on your behalf, depending on the laws in the customer’s state.
- Remote Sellers: Online businesses shipping products across state lines must be aware of varying tax obligations to avoid compliance issues.
Online Sales Tax in No-Sales-Tax States
For online businesses operating in a state without sales tax, determining whether to collect sales tax can be complex.
- Selling to Customers in Other States: If you sell to customers in states with sales tax, you may be required to collect and remit sales tax based on their location.
- Reseller Certificates: Businesses that buy goods for resale can avoid paying sales tax by using reseller certificates, but they must properly document transactions.
- Software & Digital Goods: Some states tax digital goods and services even if no physical goods are exchanged, so online businesses should verify applicable regulations.
If I’m Based in a State with No Sales Tax, Do I Have to Collect Online Sales Tax?
Yes, depending on where your customers are located. The presence of economic nexus laws means that even businesses in tax-free states may have collection obligations.
- Sales Thresholds: Many states require businesses to collect sales tax if they exceed $100,000 in revenue or 200 transactions within their borders.
- Tax Compliance Tools: Automated sales tax software can help track obligations and ensure compliance with varying state laws.
- Exemptions & Considerations: Certain products or services may be exempt from sales tax, but businesses must research each state’s rules to remain compliant.
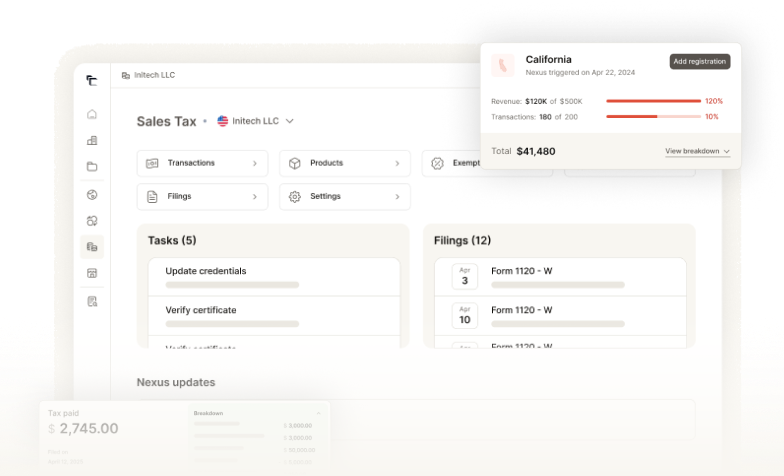
How Commenda Helps with Sales Tax Compliance
Navigating sales tax obligations across different states can be challenging, especially for businesses operating from tax-free states. Commenda provides automated sales tax solutions that help businesses:
- Track Tax Liability Anywhere: Identify when and where you need to collect sales tax based on economic nexus laws.
- Automate Tax Collection & Filing: Ensure compliance with multi-state tax requirements without manual effort.
- Simplify Cross-Border Compliance: Whether you’re based in a state with no sales tax or selling internationally, Commenda streamlines tax obligations for hassle-free operations.
By leveraging Commenda’s advanced tax automation tools, businesses can focus on growth without worrying about compliance issues.
Conclusion
While some states do not impose a sales tax, businesses and consumers should be aware of other tax structures, local regulations, and potential obligations when selling across state lines. Whether you’re a business looking to reduce tax complexities or a shopper searching for tax-free purchases, understanding the nuances of each state’s tax system is crucial for making informed financial decisions.